The Foundational Role and Evolving Landscape of Expanded Metal in Modern Industry
The industrial demand for versatile, durable, and cost-effective materials has steadily driven the prominence of expanded metal across a myriad of sectors, making expanded metal for sale a pivotal offering in the global supply chain. This unique product, characterized by its diamond-shaped openings and integral construction, offers an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, superior ventilation, and efficient light transmission, attributes critical for diverse applications ranging from robust security barriers and intricate architectural facades to high-performance filtration systems and durable walkways. The market for expanded metal is experiencing dynamic shifts, influenced by advancements in manufacturing technology, the increasing adoption of sustainable building practices, and the growing complexity of industrial infrastructure projects that demand materials capable of extreme performance under various environmental stressors. Modern trends indicate a significant surge in demand for lightweight yet structurally sound materials, positioning expanded metal as an indispensable component in contemporary engineering and design. The versatility of expanded metal, available in a broad spectrum of materials including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and galvanized steel, ensures its adaptability to specific corrosive environments, temperature extremes, and load-bearing requirements. Furthermore, the aesthetic appeal of certain expanded mesh patterns has propelled its use in decorative and design-focused applications, broadening its market beyond purely functional industrial uses. The global industrial landscape is continuously evolving, with a strong emphasis on efficiency, safety, and longevity of materials. This necessitates a deep understanding of product specifications, material science, and manufacturing integrity when sourcing expanded metal, as substandard products can lead to critical structural failures, compromised safety, and significant financial repercussions. Consequently, procurement decisions are increasingly informed by rigorous technical evaluations, long-term performance guarantees, and adherence to international quality standards, reflecting a mature market that values expertise and reliability above all. The inherent design of expanded metal – a single piece of metal that has been slit and stretched without welding – eliminates the risk of joint failure, offering unparalleled structural integrity and extended operational lifespans in demanding applications. As industries worldwide strive for optimized operational costs and enhanced sustainability, the intrinsic value proposition of expanded metal as a durable, resource-efficient, and highly functional material continues to grow, underpinning its critical role in facilitating progress across sectors like petrochemical, metallurgy, construction, and automotive. The strategic availability of expanded metal for sale directly supports these industry needs, providing a readily accessible solution for diverse engineering challenges.
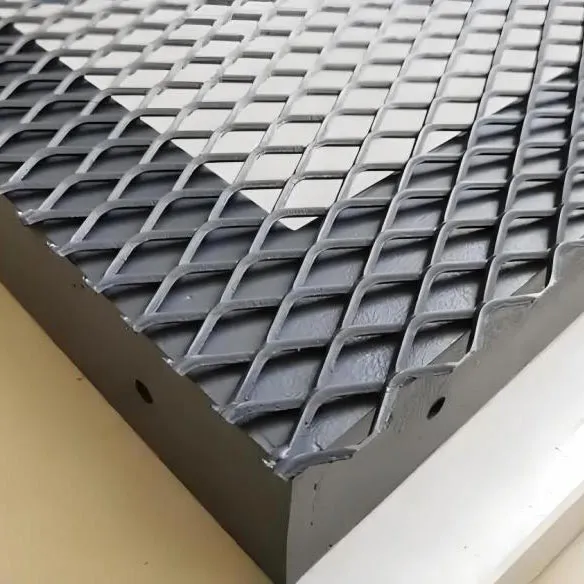

Precision Engineering: The Meticulous Manufacturing Process of Expanded Metal
The production of expanded metal is a sophisticated cold-forming process that transforms a solid sheet of metal into a mesh-like structure without material loss, differentiating it significantly from welding or weaving. This precise manufacturing sequence begins with the selection of high-grade raw materials, typically coils or sheets of carbon steel, stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316), aluminum alloys (e.g., 1050, 3003, 5052), galvanized steel, or more specialized metals like nickel, copper, and titanium, chosen based on the intended application's demands for corrosion resistance, strength, and environmental compatibility. The initial phase involves feeding the metal sheet into an expanding machine, where a series of synchronized knives or dies slit the metal and then simultaneously stretch or expand it. This slitting and stretching action creates diamond-shaped openings, known as meshes, and leaves an unbroken, integral bond between the strands, forming a strong, monolithic piece of expanded mesh. Unlike woven mesh, which relies on interlocking wires, or welded mesh, which can suffer from weld point fatigue, the integral nature of expanded metal means there are no weak points to fail under stress, significantly enhancing its durability and lifespan. The manufacturing process allows for immense control over key parameters such as the Short Way of Diamond (SWD) and Long Way of Diamond (LWD), which define the dimensions of the mesh openings, and the strand width and thickness, which determine the overall robustness and open area percentage of the final product. Quality control is paramount at every stage. Raw materials are rigorously inspected for chemical composition and mechanical properties to ensure they meet industry standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and EN (European Standards). During the expansion process, continuous monitoring ensures dimensional accuracy, uniform mesh patterns, and consistent strand integrity. Post-expansion, products undergo thorough visual inspections for defects, burrs, or inconsistencies, followed by precise measurements of mesh sizes, thickness, and overall dimensions. For specialized applications, additional testing may include tensile strength, yield strength, and specific corrosion resistance tests, all aligned with standards like ISO 9001 for quality management systems. The lifespan of expanded steel mesh is exceptional, often exceeding decades, especially when appropriate material selection and protective coatings (like galvanization, powder coating, or anodizing) are applied. This longevity contributes to its cost-effectiveness over time, making it a sustainable choice. This robust and versatile material finds extensive application across critical sectors: in petrochemical industries for platforms, walkways, and catalyst support grids where its non-slip surface and open area facilitate drainage and air flow while providing structural integrity; in metallurgy for furnace guards and material handling systems due to its high heat resistance and strength; and in water treatment and drainage systems as filter screens and strainers, benefiting from its precise filtration capabilities and corrosion resistance. The inherent design advantages, such as enhanced ventilation and drainage, coupled with superior structural strength derived from its unique manufacturing process, make expanded metal for sale a preferred choice in environments where safety, longevity, and operational efficiency are non-negotiable.
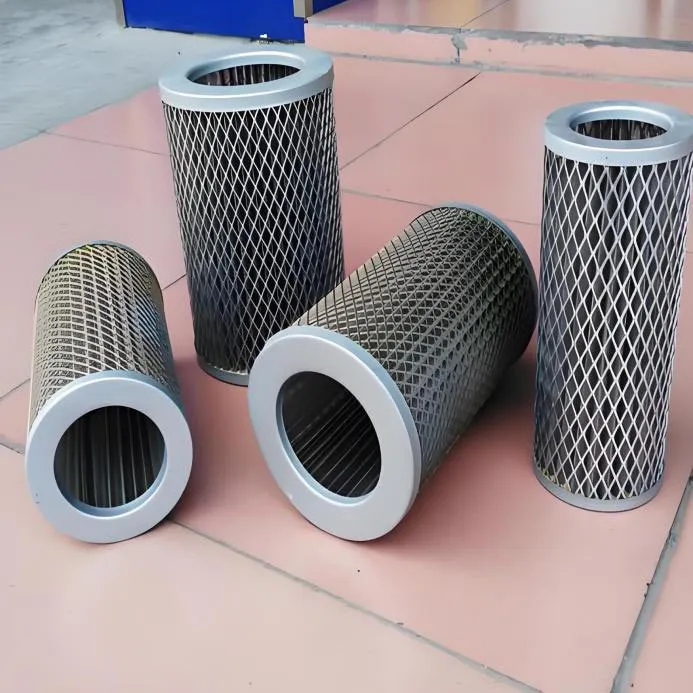

Understanding Key Technical Parameters and Specifications of Expanded Metal
When sourcing expanded metal for sale, a detailed understanding of its technical parameters is crucial for selecting the appropriate product that meets specific application requirements and performance criteria. These parameters define the physical characteristics and functional attributes of the expanded mesh, directly impacting its strength, open area, weight, and aesthetic appeal. Key specifications include the material type, which dictates corrosion resistance, conductivity, and strength (e.g., A36 carbon steel for structural applications, 316L stainless steel for marine environments, 6061-T6 aluminum for lightweight needs). The strand width, referring to the amount of metal that runs along the short dimension of the diamond opening, and the strand thickness (or gauge), representing the thickness of the base metal sheet from which the expanded metal is produced, are fundamental in determining the mesh's load-bearing capacity and rigidity. The Short Way of Diamond (SWD) is the dimension of the opening measured across the shorter diagonal, while the Long Way of Diamond (LWD) is the dimension measured across the longer diagonal. These two measurements are critical for defining the size and shape of the mesh openings and thus the degree of light, air, or fluid passage. The overall thickness of the expanded metal, particularly important for flattened expanded metal (FEM) where the strands and bonds lie in the same plane, influences its stackability and integration into design assemblies. Mesh size, often expressed as SWD x LWD, defines the pattern of the expanded metal (e.g., 1/2" x 1" expanded mesh). The open area percentage, a critical functional parameter, quantifies the amount of open space within the mesh, directly affecting ventilation, filtration efficiency, and light transmission. A higher open area allows for greater flow, while a lower open area provides more privacy or structural integrity. Weight per square meter or foot is essential for calculating shipping costs, structural load, and overall project budgeting, reflecting the density and material volume of the expanded metal. Finishes, such as hot-dip galvanization for enhanced corrosion protection, powder coating for aesthetic customization and added durability, or anodizing for aluminum, further extend the product's applicability and lifespan. For example, a common specification might be a 4x8 expanded metal sheet, referring to a standard sheet dimension, made from 1/2" x 1" #13 carbon steel, which signifies specific SWD and LWD dimensions and a particular strand gauge suitable for general industrial walkways. Understanding how these parameters interact is vital; a denser mesh (smaller SWD/LWD, thicker strands) will have less open area but greater strength, while a lighter mesh will offer more open area and reduced weight. Precision in these specifications ensures that the product performs as expected in its intended environment, whether it's for heavy-duty industrial platforms requiring high load capacity and anti-slip properties, or for architectural screens demanding specific light diffusion and aesthetic qualities. The data provided below represents typical expanded metal specifications, but it's important to note that customization is widely available to meet unique project demands.
| Parameter | Description | Typical Range/Value | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Base metal used for expansion | Carbon Steel (A36, Q235), Stainless Steel (304, 316), Aluminum (1050, 3003, 5052), Galvanized Steel | Corrosion resistance, strength, weight, cost |
| SWD (Short Way of Diamond) | Measurement across the shorter diagonal of the opening | 3mm - 75mm (0.125" - 3") | Opening size, filtration capability, light/air flow |
| LWD (Long Way of Diamond) | Measurement across the longer diagonal of the opening | 6mm - 150mm (0.25" - 6") | Opening size, pattern design, structural rigidity |
| Strand Width | Amount of metal in each strand | 0.5mm - 8mm (0.02" - 0.315") | Strength, open area, weight |
| Strand Thickness (Gauge) | Original thickness of the metal sheet | 0.3mm - 6mm (0.012" - 0.25") | Structural integrity, load-bearing capacity |
| Overall Thickness | Total thickness of the expanded metal sheet | Depends on strand thickness and mesh configuration (up to 20mm for raised, same as strand thickness for flattened) | Compatibility with mounting systems, aesthetics |
| Open Area Percentage | Ratio of open space to total area | 20% - 90% (Higher for decorative, lower for security) | Ventilation, light transmission, fluid flow, privacy |
| Weight per Unit Area | Weight per square meter/foot | 1.5 kg/m² - 25 kg/m² (0.3 lbs/ft² - 5 lbs/ft²) | Structural load, shipping costs, ease of handling |
| Finish | Surface treatment applied post-expansion | Mill finish, Hot-dip Galvanized, Electro-galvanized, Powder Coated, Anodized, PVC Coated | Corrosion protection, aesthetics, friction coefficient |
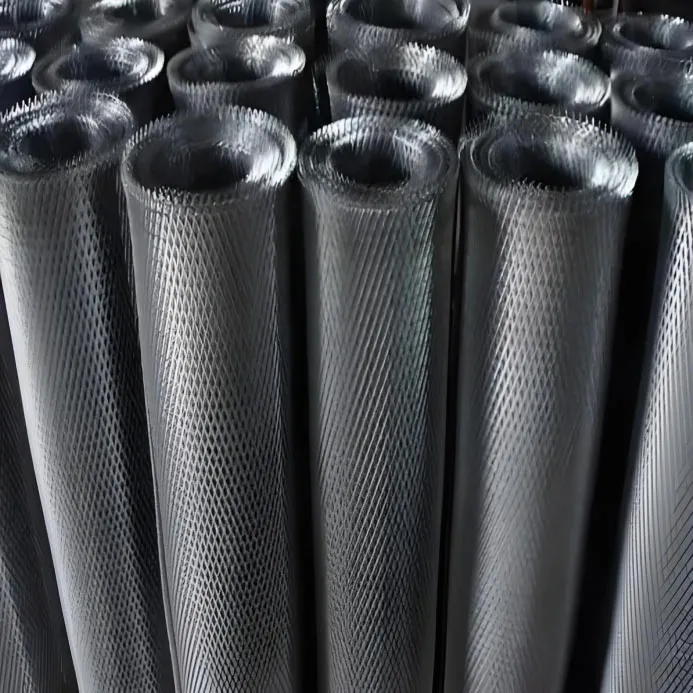

Diverse Applications and Strategic Advantages of Expanded Metal Across Industries
The inherent versatility and robust characteristics of expanded metal enable its widespread adoption across a vast array of industries, each leveraging its unique properties to enhance functionality, safety, and cost-efficiency. In the construction and architectural sectors, expanded metal is indispensable for walkways, stair treads, mezzanines, and safety barriers due to its anti-slip surface and high load-bearing capacity. Its open mesh design prevents the accumulation of water, snow, and debris, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial environments. Furthermore, architectural expanded mesh is increasingly specified for building facades, sunscreens, and decorative elements, offering both aesthetic appeal and practical benefits such as light diffusion and ventilation. For instance, large-scale projects often utilize 4x8 expanded metal sheets for uniform paneling, showcasing its adaptability for significant architectural features. The security industry heavily relies on expanded metal for fencing, window guards, and secure enclosures, as its monolithic construction makes it exceptionally resistant to cutting and tampering, providing a formidable physical barrier without obstructing visibility. In the transportation sector, particularly automotive and rail, expanded steel mesh is employed for radiator grilles, air intakes, and filtration components, benefiting from its lightweight nature, excellent airflow, and resistance to impact. Its use in vehicle flooring and protective guards underscores its durability under dynamic stresses. The petrochemical and energy sectors utilize expanded metal extensively in oil and gas platforms, refineries, and power plants for equipment guarding, access platforms, and elevated walkways. The material's corrosion resistance, especially when stainless steel or galvanized variants are used, ensures longevity in harsh chemical environments, contributing to operational safety and reducing maintenance downtime. For water treatment facilities and drainage systems, expanded metal serves as effective filter screens, strainers, and grates, preventing debris accumulation while allowing efficient fluid passage. Its inherent resistance to biological growth and chemical degradation in water makes it a preferred material for such critical infrastructure. Agriculture also benefits from expanded mesh in applications like grain drying floors, animal enclosures, and machinery guards, where its open design facilitates air circulation and easy cleaning. The ability of expanded metal to dissipate heat efficiently makes it valuable in electronic enclosures and equipment cooling applications, preventing overheating and extending the lifespan of sensitive components. From a technical advantages perspective, expanded metal boasts an impressive strength-to-weight ratio, which reduces structural load and material consumption, leading to lower installation costs and enhanced design flexibility. Its single-piece construction eliminates welds and weaves, preventing common failure points associated with other mesh types and guaranteeing superior integrity. The diamond pattern inherently offers excellent anti-slip properties, significantly enhancing safety in industrial walkways and platforms. Furthermore, the high percentage of open area allows for optimal light, air, and fluid passage, which is crucial for ventilation, filtration, and vision panels. Environmentally, the manufacturing process of expanded metal is inherently efficient as it produces no material waste, utilizing the entire sheet. This sustainability factor, combined with its long lifespan and recyclability, aligns perfectly with contemporary green building and manufacturing initiatives. The anti-corrosion properties, particularly in stainless steel or hot-dip galvanized versions of expanded metal for sale, ensure resilience in aggressive environments, minimizing the need for frequent replacement and contributing to lower lifecycle costs. The inherent rigidity and formability of expanded metal allow for complex shaping and fabrication, accommodating custom designs and challenging installation requirements with ease.
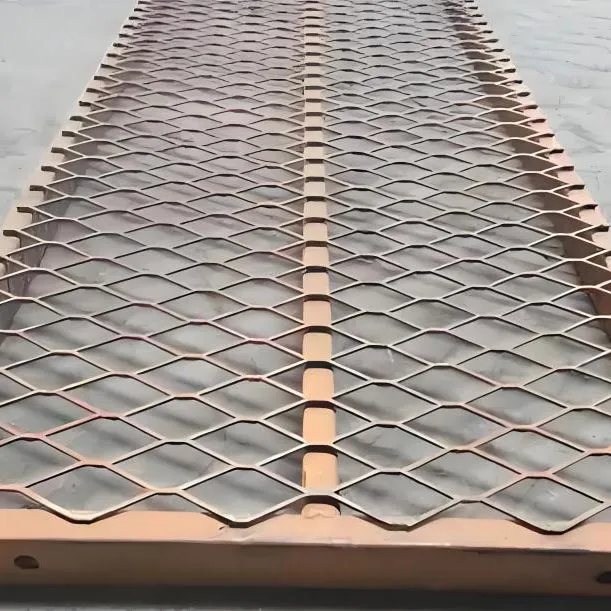

Strategic Selection: Manufacturer Comparison and Tailored Expanded Metal Solutions
The process of selecting a supplier for expanded metal for sale is a critical decision that significantly impacts project success, material performance, and overall cost-efficiency. It goes beyond simply comparing prices; it necessitates a comprehensive evaluation of a manufacturer's expertise, product quality, customization capabilities, and post-sales support. A reputable manufacturer distinguishes itself through stringent quality control measures, adherence to international standards (like ISO 9001 for quality management and ASTM for material specifications), and transparent material sourcing. They should possess a deep understanding of metallurgy, mechanical engineering, and specific industry applications to advise clients on the most suitable expanded metal product for their unique needs. When evaluating manufacturers, consider their years of experience in the industry, which often correlates with accumulated knowledge and a proven track record of successful project deliveries. Look for evidence of authoritative certifications and partnerships with leading raw material suppliers, which assure material quality and traceability. For example, a supplier who can provide detailed mill certificates for their steel or aluminum feedstock demonstrates commitment to transparency and quality. Customization is a cornerstone of modern industrial supply. While standard sizes like 4x8 expanded metal sheets are readily available, many projects demand bespoke solutions. A superior manufacturer offers extensive customization options, including varying material types (e.g., specific grades of stainless steel for corrosive environments, or architectural aluminum for aesthetic applications), diverse mesh patterns (e.g., diamond, hexagonal, decorative), and a wide range of strand widths and thicknesses to achieve specific strength-to-weight ratios or open area percentages. Furthermore, the ability to provide specialized finishes such as hot-dip galvanization for superior corrosion resistance, PVC coating for added protection and color, or various powder coat finishes for aesthetic and durability purposes, highlights a manufacturer's comprehensive capability. For unique applications, the supplier should be able to offer custom cutting, forming, and fabrication services to precisely match project blueprints, minimizing waste and simplifying on-site installation. Consider a case where a client required specialized expanded mesh for a highly corrosive chemical processing plant. Instead of a standard carbon steel, the manufacturer recommended and fabricated custom 316L stainless steel expanded metal with a specific strand configuration and overall thickness to withstand aggressive chemical exposure and heavy foot traffic, demonstrating their problem-solving capability and technical expertise. Another instance might involve an architectural firm seeking a unique façade for a commercial building, requiring custom-patterned aluminum expanded metal with a specific anodized finish to achieve a particular visual effect and light diffusion. A proficient manufacturer would be able to translate these complex design specifications into a tangible product, providing samples and detailed technical drawings for approval. Ultimately, the choice of manufacturer for expanded metal for sale should be a strategic partnership based on trust, demonstrated technical proficiency, and a shared commitment to project excellence. A manufacturer’s ability to offer comprehensive technical support, from initial design consultation and material selection to post-delivery troubleshooting, is invaluable for ensuring optimal product integration and long-term performance, reinforcing their role as an authoritative and reliable partner in industrial procurement.

Ensuring Trust: Quality Assurance, Delivery Logistics, and Comprehensive Customer Support for Expanded Metal
The foundation of a reliable supplier relationship for expanded metal for sale rests firmly on a robust framework of quality assurance, efficient delivery logistics, and comprehensive customer support. For B2B buyers, these elements are not merely add-ons but essential components that mitigate risk, ensure project timelines are met, and guarantee the long-term performance of the purchased material. A reputable manufacturer employs multi-stage quality control protocols that begin with the certification of raw materials, ensuring they meet specified chemical compositions and mechanical properties according to standards like ASTM A1011/A1011M for steel or ASTM B209 for aluminum. This initial verification prevents downstream issues and is crucial for product integrity. During the manufacturing process, advanced laser measurement tools and skilled technicians continuously monitor the consistency of mesh patterns, strand dimensions (SWD, LWD, strand width, and thickness), and overall sheet dimensions, ensuring every sheet of expanded metal conforms to precise specifications. Post-production, each batch undergoes final inspection for surface defects, burrs, and adherence to specified finishes, such as the uniform coating thickness for hot-dip galvanized or powder-coated products. Test data, including material strength, open area percentages, and corrosion resistance reports, should be readily available and align with relevant industry standards such as ISO 9001 quality management principles. This meticulous attention to detail at every stage underscores the manufacturer's expertise and authoritative commitment to delivering only the highest quality product. Beyond manufacturing, the trustworthiness of a supplier is significantly demonstrated by their delivery capabilities and commitment to timelines. For large-scale industrial projects, on-time delivery of materials like expanded steel mesh is paramount to avoid costly delays. A reliable supplier will offer transparent delivery schedules, clear communication channels for order tracking, and robust packaging solutions to protect the expanded metal during transit, preventing damage and ensuring it arrives ready for installation. This includes secure crating for flat sheets and appropriate bundling for rolls of expanded mesh. Global reach, established logistics networks, and partnerships with reputable freight carriers are indicative of a supplier's capacity to manage complex international shipments efficiently and reliably, minimizing lead times and providing peace of mind for buyers worldwide. Furthermore, comprehensive customer support is a distinguishing factor for a truly trustworthy supplier. This extends beyond merely processing orders to offering technical assistance, troubleshooting advice, and post-sale support. A dedicated customer service team should be accessible to address inquiries regarding product specifications, application suitability, installation guidance, and warranty claims. Providing an explicit quality warranty and a clear return policy instills confidence, assuring buyers that the manufacturer stands behind their product. An example of exceptional service would be a supplier who, upon receiving a query about optimal cutting techniques for 4x8 expanded metal for a specific onsite fabrication, provides detailed technical diagrams and best practice recommendations, demonstrating their commitment to client success beyond the point of sale. A well-structured Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) section online further empowers customers by providing immediate answers to common concerns about product characteristics, maintenance, and usage. For instance, questions regarding the difference between standard and flattened expanded metal, or the most effective methods for cleaning specific finishes, can be pre-emptively addressed. This proactive approach to support, combined with rigorous quality control and dependable logistics, consolidates a supplier’s reputation as a reliable and expert partner in the industrial supply chain.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Expanded Metal for Sale
Understanding the common queries related to expanded metal for sale is essential for both buyers and suppliers to ensure clarity and effective project execution. This FAQ section addresses typical questions that arise when specifying, purchasing, and utilizing expanded metal products. A common question revolves around the difference between "standard" (or raised) and "flattened" expanded metal. Standard expanded metal, directly from the expanding machine, has raised strands and bonds, creating a slip-resistant surface that is ideal for walkways, platforms, and stair treads where traction is paramount. Flattened expanded metal (FEM) is produced by cold rolling standard expanded metal, which flattens the strands and bonds into a uniform plane, resulting in a smooth, flat surface. This process also slightly elongates the diamond openings and reduces the overall thickness. FEM is preferred for architectural applications, furniture, shelving, or anywhere a smooth surface and aesthetic appeal are desired, as it lays flat and is easier to handle. Another frequently asked question pertains to the selection of the correct material. The choice of material for expanded mesh depends critically on the intended application's environment. For general industrial use and structural components where corrosion is not a major concern, carbon steel is often chosen for its strength and cost-effectiveness. For outdoor applications or mild corrosive environments, galvanized steel (either electro-galvanized or hot-dip galvanized) offers enhanced rust protection. For marine environments, chemical processing plants, or applications requiring high hygiene (e.g., food processing), stainless steel (e.g., 304 or 316) is preferred due to its superior corrosion resistance. Aluminum is selected when lightweight properties, high conductivity, or specific aesthetic finishes (like anodizing) are required. Buyers often inquire about the meaning of "mesh size" and its impact. Mesh size, typically denoted by SWD (Short Way of Diamond) x LWD (Long Way of Diamond), defines the dimensions of the diamond-shaped openings. These measurements are crucial as they directly influence the open area percentage, which in turn affects airflow, light transmission, filtration capability, and the ability to prevent objects from passing through. For instance, a smaller mesh size might be chosen for security screens or fine filtration, while a larger mesh size is suitable for heavy-duty grates or decorative panels requiring more openness. Questions regarding the load-bearing capacity of expanded metal for sale are also common. The strength of expanded metal is determined by a combination of factors including the original material's gauge (thickness), the strand width, and the mesh size (SWD and LWD). Thicker gauges and wider strands generally yield higher load-bearing capacities. Reputable manufacturers provide load charts and technical data based on engineering calculations and testing, allowing engineers to specify the correct expanded metal for structural applications. Furthermore, inquiries about available finishes and their benefits are frequent. Beyond mill finish, common options include hot-dip galvanizing, which provides a thick, sacrificial zinc coating for excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and harsh environments. Powder coating offers a wide range of colors for aesthetic customization and provides an additional layer of protection against chips and scratches. Anodizing is a finish specifically for aluminum, enhancing its natural corrosion resistance and allowing for various decorative colors. Lastly, questions about custom fabrication capabilities are crucial. Most industrial buyers require more than just standard sheet sizes; they need custom cuts, specific dimensions like the non-standard 4x8 expanded metal equivalents in different units, or even forming and welding for complex assemblies. A skilled manufacturer can provide detailed technical drawings and offer pre-fabrication services to ensure the expanded metal integrates seamlessly into the final project, reducing on-site labor and material waste. These FAQs highlight the technical depth required in sourcing expanded metal and emphasize the importance of partnering with knowledgeable suppliers.

Conclusion: The Enduring Value and Future of Expanded Metal in Industrial Excellence
The expansive utility and intrinsic advantages of expanded metal firmly establish its position as a cornerstone material in a multitude of industrial and architectural applications. From enhancing safety on petrochemical platforms with its non-slip surfaces and structural integrity, to providing innovative aesthetic and functional solutions in modern building facades, the versatility of expanded metal is unparalleled. Its unique manufacturing process, which transforms a solid sheet into a robust, monolithic mesh without material loss, results in an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, superior ventilation, and efficient light and fluid transmission. This inherent efficiency and durability translate directly into long-term cost savings through extended product lifespans, reduced maintenance, and optimal resource utilization, aligning with global trends towards sustainable engineering practices. The ability to precisely control technical parameters such as SWD, LWD, strand width, and thickness, coupled with the availability of diverse materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, ensures that there is an ideal expanded metal for sale solution for virtually any demanding environment or aesthetic requirement. Furthermore, the commitment of leading manufacturers to stringent quality control, adherence to international standards like ISO and ASTM, and the provision of comprehensive technical support and customization services, underpins the reliability and trustworthiness of expanded metal products in critical applications. As industries continue to evolve, driven by demands for increased efficiency, enhanced safety, and greater environmental responsibility, the role of expanded metal is poised to grow. Innovations in materials science and manufacturing techniques will likely lead to even lighter, stronger, and more specialized expanded metal products, further broadening its application spectrum. The strategic integration of standard sizes, such as the widely applicable 4x8 expanded metal sheets, alongside bespoke, custom-fabricated solutions, empowers engineers and designers to overcome complex challenges and realize ambitious projects. The enduring value of expanded metal lies not only in its robust physical properties but also in its economic viability and environmental conscientiousness, making it an indispensable component for driving industrial excellence and fostering sustainable development across the globe. As a critical building block for infrastructure, safety, and aesthetic design, expanded metal remains a vital investment for businesses seeking durable, high-performance, and cost-effective material solutions.
References and Further Reading
- ASTM International. (2020). A1011/A1011M-20 Standard Specification for Steel, Sheet, and Strip, Hot-Rolled, Carbon, Structural, High-Strength Low-Alloy, High-Strength Low-Alloy with Improved Formability, and Ultra-High Strength. This standard provides detailed specifications for steel sheets, the primary raw material for expanded metal.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). (2015). ISO 9001:2015 Quality management systems — Requirements. A foundational standard for quality management, critical for manufacturing excellence in expanded metal production.
- Expanded Metal Manufacturers Association (EMMA). (Accessed 2023). Industry guidelines and technical resources on expanded metal. While a direct academic link is not always available, EMMA provides authoritative information on product specifications and applications. Relevant information can often be found on member websites or industry portals for expanded metal. For general industry best practices, a search on "Expanded Metal Association technical guidelines" can yield relevant white papers.
- Technical Guide: Expanded Metal Design and Fabrication. (Various publications from manufacturers or engineering firms). For example, a common resource is "Expanded Metal Technical Manuals" provided by leading suppliers, which often cite compliance with industrial engineering principles and standards. These resources are typically found on the technical sections of supplier websites.
Post time: Aug . 10, 2025 08:40